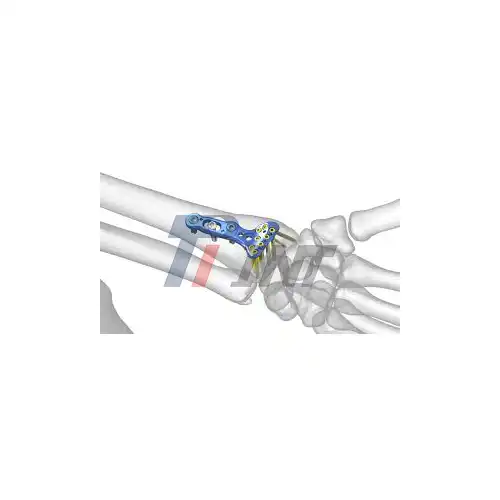
Understanding Complex Hand Bone Fractures
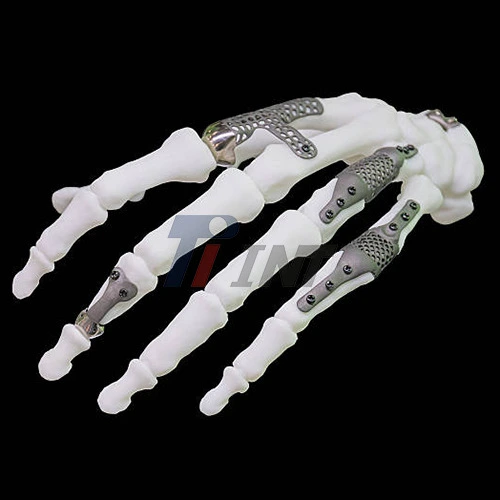
Some time recently we plunged into the specifics of titanium plate hand surgery; it's pivotal to get the nature of complex hand bone breaks. The human hand is a complicated structure, composed of 27 bones, various joints, and an organize of ligaments and tendons. This complexity makes hand wounds especially challenging to treat.
Complex hand bone fractures typically involve multiple bone fragments, joint surfaces, or extend into surrounding soft tissues. These injuries can result from various causes, including:
- High-impact trauma (e.g., car accidents or sports injuries)
- Crushing injuries
- Falls on an outstretched hand
- Machinery accidents
Traditional treatment methods, such as casting or external fixation, may not provide adequate stability or alignment for complex fractures. This is where titanium plate hand surgery comes into play, offering a more robust and precise solution for these challenging cases.
The Marvels of Titanium in Medical Applications
Titanium has emerged as a game-changer in the medical field, particularly in orthopedic and maxillofacial surgeries. Its unique properties make it an ideal material for implants and surgical hardware. Let's explore why titanium is the material of choice for hand bone fracture fixation:
1. Biocompatibility: Titanium is renowned for its excellent biocompatibility. It rarely causes allergic reactions or rejection by the body, making it safe for long-term implantation.
2. Strength-to-weight ratio: Despite being lightweight, titanium boasts impressive strength. This allows for the creation of thin, low-profile plates that provide robust support without adding unnecessary bulk.
3. Corrosion resistance: Titanium's natural resistance to corrosion ensures the longevity of implants, reducing the risk of complications over time.
4. Osseointegration: Titanium has the unique ability to bond directly with bone tissue, a process known as osseointegration. This property enhances the stability of the implant and promotes faster healing.
5. Non-ferromagnetic: Unlike some other metals, titanium is non-ferromagnetic, allowing patients to undergo MRI scans safely after surgery.
The Titanium Plate Hand Surgery Procedure
Titanium plate hand surgery is a sophisticated procedure that requires skill, precision, and a deep understanding of hand anatomy. Here's an overview of the typical surgical process:
1. Preoperative planning: The surgeon carefully evaluates the fracture using X-rays, CT scans, or MRI to determine the optimal placement of the titanium plate.
2. Anesthesia: Depending on the complexity of the fracture and patient factors, the procedure may be performed under general anesthesia or regional nerve block.
3. Incision and exposure: The surgeon makes a carefully planned incision to access the fractured bone while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
4. Fracture reduction: The bone fragments are meticulously realigned to their proper anatomical position.
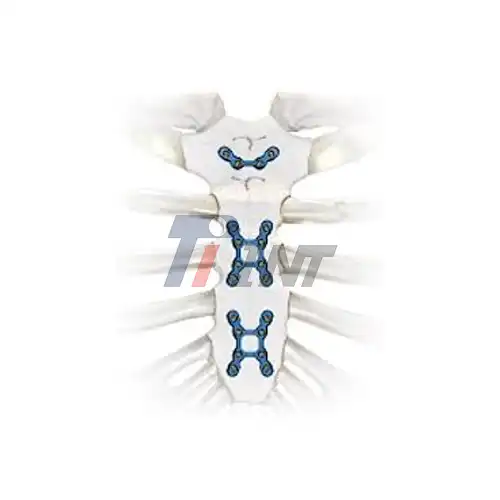
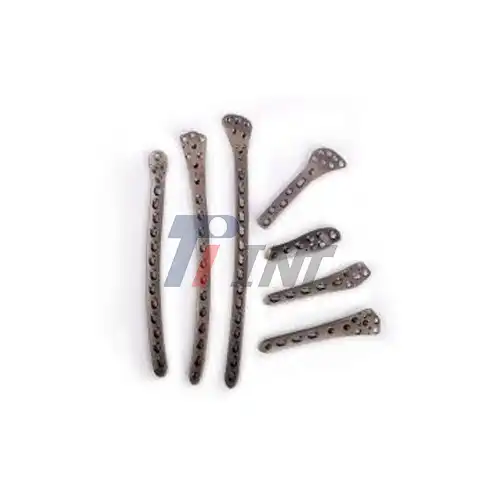
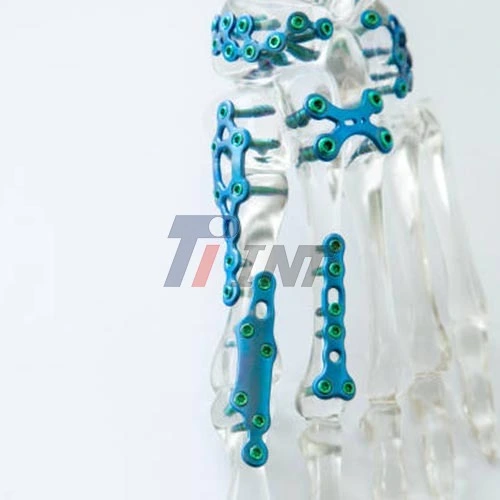
5. Plate application: A titanium plate of appropriate size and shape is selected and carefully positioned over the fracture site. The plate is then secured to the bone using titanium screws.
6. Additional fixation: In some cases, additional support may be provided using smaller plates, screws, or wires to ensure optimal stability.
7. Wound closure: Once the fracture is securely fixated, the incision is closed using sutures or staples.
8. Post-operative care: The hand is typically immobilized in a splint or cast for a period to protect the surgical site and promote healing.
Recovery and Rehabilitation After Titanium Plate Hand Surgery
The journey to full recovery after titanium plate hand surgery is a collaborative effort between the patient, surgeon, and rehabilitation specialists. Here's what patients can typically expect during the recovery process:
1. Immediate post-operative period: The hand is usually immobilized in a splint or cast to protect the surgical site and allow initial healing. Pain management and elevation of the hand are crucial during this phase.
2. Early mobilization: Depending on the fracture's stability and the surgeon's assessment, gentle range of motion exercises may begin as early as a few days after surgery. This early mobilization is often possible thanks to the robust fixation provided by titanium plates.
3. Progressive rehabilitation: As healing progresses, patients work with hand therapists to gradually increase the intensity and complexity of exercises. This may include:
- Passive and active range of motion exercises
- Strengthening exercises
- Scar management techniques
- Desensitization exercises for nerve-related symptoms
4. Return to activities: The timeline for returning to daily activities and work varies depending on the fracture's severity and the patient's occupation. Most patients can resume light activities within 6-8 weeks, with full recovery taking 3-6 months or longer for complex cases.
5. Long-term follow-up: Periodic check-ups with the surgeon are essential to monitor healing and address any concerns. In most cases, titanium plates are left in place permanently unless they cause irritation or other issues.
Advancements in Titanium Plate Technology for Hand Surgery
The field of orthopedic implant technology is constantly evolving, and titanium plates for hand surgery are no exception. Recent advancements have further improved the efficacy and patient outcomes of titanium plate hand surgery:
1. Low-profile designs: Modern titanium plates are increasingly thin and contoured, reducing the risk of soft tissue irritation and tendon adhesions.
2. Variable-angle locking systems: These innovative plate designs allow surgeons to adjust the angle of screw placement, providing greater flexibility in addressing complex fracture patterns.
3. Surface modifications: Some titanium plates feature specialized surface treatments that enhance osseointegration and reduce the risk of infection.
4. 3D-printed custom implants: For particularly complex cases, 3D-printed titanium plates can be custom-designed to match the patient's unique anatomy perfectly.
5. Bioabsorbable coatings: Research is ongoing into bioabsorbable coatings for titanium plates, which may help reduce long-term complications and eliminate the need for implant removal.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While titanium plate hand surgery is generally safe and effective, it's important for patients and healthcare providers to be aware of potential risks and considerations:
1. Infection: Although rare, surgical site infections can occur. Proper sterilization techniques and perioperative antibiotic protocols help minimize this risk.
2. Hardware irritation: In some cases, patients may experience discomfort or irritation from the titanium plate, particularly in areas with thin soft tissue coverage.
3. Tendon adhesions: Scar tissue formation around the plate can potentially lead to tendon adhesions, affecting hand mobility. This risk is mitigated by modern low-profile plate designs and proper rehabilitation.
4. Nonunion or malunion: While less common with titanium plate fixation, there's still a small risk of the fracture not healing properly.
5. Nerve or vascular injury: The complex anatomy of the hand means there's a risk of damaging nerves or blood vessels during surgery. This risk is minimized by careful surgical planning and technique.
6. Metal sensitivity: Although extremely rare with titanium, some patients may develop sensitivity to the implant material.
Conclusion
As we continue to push the boundaries of medical science, the future of hand fracture treatment looks promising. With ongoing research and development in implant technology and surgical techniques, we can expect even better outcomes for patients suffering from complex hand injuries.
For medical professionals and institutions seeking high-quality titanium plates hand surgery, Baoji INT Medical Titanium Co., Ltd. stands as a reliable partner. With over 30 years of experience in the research, development, and production of medical titanium materials, INT offers a comprehensive range of titanium products tailored to the needs of the medical field. To learn more about their medical titanium products or to discuss your specific requirements, don't hesitate to reach out to their team at export@tiint.com.










 2025-09-05 15:56:25
2025-09-05 15:56:25


_1752463076575.webp)