Understanding Mandibular Fractures and Titanium Plate Fixation
The mandible, or lower jaw, is a U-shaped bone that plays a crucial role in various functions, including speaking, chewing, and maintaining facial symmetry. Due to its prominent position and frequent exposure to trauma, the mandible is susceptible to fractures. Mandibular fractures can occur in different locations, such as the symphysis, body, angle, ramus, or condyle, each presenting unique challenges in treatment.
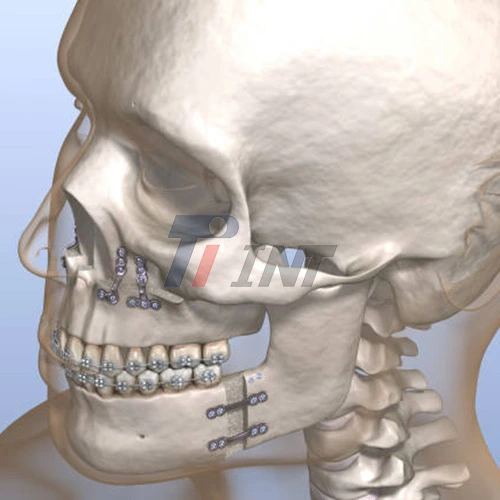
Titanium plate for mandibular fracture has revolutionized the management of mandibular fractures. This technique involves using titanium plates and screws to stabilize the fractured bone segments, promoting proper alignment and facilitating healing. Titanium is the material of choice due to its exceptional biocompatibility, strength, and corrosion resistance.
The process of titanium plate fixation for mandibular fractures typically involves the following steps:
- Surgical exposure of the fracture site
- Reduction of the fractured bone segments to their anatomical position
- Application of titanium plates across the fracture line
- Securing the plates with titanium screws
- Closure of the surgical site
The specific configuration and number of plates used depend on the fracture location, pattern, and severity. Surgeons carefully plan the placement of titanium plates to ensure optimal stability and minimize interference with adjacent structures.
Advantages of Titanium Plate Fixation in Mandibular Fracture Treatment
Titanium plate fixation offers numerous advantages in the treatment of mandibular fractures, contributing to its widespread adoption in maxillofacial surgery. Some key benefits include:
- Stability and Rigidity: Titanium plates provide excellent stability to the fractured segments, allowing for immediate function and promoting faster healing. The rigid fixation minimizes micromovement at the fracture site, which is essential for proper bone union.
- Biocompatibility: Titanium is highly biocompatible, meaning it is well-tolerated by the human body. This property reduces the risk of adverse reactions and promotes better integration with surrounding tissues.
- Corrosion Resistance: Titanium's exceptional corrosion resistance ensures long-term stability of the fixation, reducing the likelihood of hardware-related complications.
- Reduced Need for Intermaxillary Fixation: Unlike traditional wire fixation methods, titanium plate fixation often eliminates or significantly reduces the need for prolonged intermaxillary fixation (wiring the jaws shut), allowing patients to resume normal oral function sooner.
- Improved Aesthetics: The precise reduction and fixation achieved with titanium plates help maintain facial symmetry and contour, leading to better aesthetic outcomes.
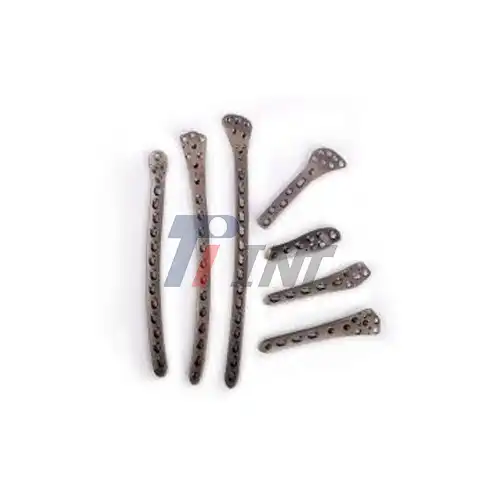
- Versatility: Titanium plate for mandibular fracture are available in various sizes and configurations, allowing surgeons to address different types of mandibular fractures effectively.
- Reduced Infection Risk: The stability provided by titanium plates minimizes soft tissue irritation and reduces the risk of infection compared to other fixation methods.
Clinical Effectiveness and Patient Outcomes
Numerous clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of titanium plate fixation in treating mandibular fractures. Research has shown that this technique leads to high success rates, with excellent bone healing and restoration of mandibular function.
A comprehensive review of literature reveals several key findings regarding the clinical effectiveness of titanium plate fixation for mandibular fractures:
- High Union Rates: Studies consistently report high rates of bone union following titanium plate fixation, with many showing success rates above 95%.
- Reduced Complication Rates: Compared to other fixation methods, titanium plate fixation is associated with lower rates of complications such as malunion, nonunion, and infection.
- Faster Recovery: Patients treated with titanium plate for mandibular fracture often experience faster recovery times and earlier return to normal function compared to traditional methods.
- Improved Occlusion: The precise reduction and stable fixation achieved with titanium plates contribute to better restoration of dental occlusion.
- Patient Satisfaction: Many studies report high levels of patient satisfaction with titanium plate fixation, citing factors such as reduced discomfort and faster return to normal activities.
While titanium plate fixation has shown excellent results in most cases, it's important to note that outcomes can vary depending on factors such as fracture severity, patient compliance, and surgical technique. Proper patient selection and meticulous surgical planning are crucial for achieving optimal results.
Surgeons must consider various factors when deciding on the use of titanium plates for mandibular fracture treatment, including:
- Fracture location and pattern
- Presence of comminution or bone loss
- Patient's overall health and healing capacity
- Presence of infection or contamination
- Need for future imaging studies (e.g., MRI compatibility)
Despite its many advantages, titanium plate fixation is not without potential complications. Some possible issues include:
- Hardware-related complications (e.g., screw loosening, plate exposure)
- Infection
- Nerve injury
- Malocclusion
- Thermal sensitivity
However, these complications are relatively rare when the procedure is performed by experienced surgeons following proper protocols. Many of these issues can be managed conservatively or with minor interventions.
Recent advancements in titanium plate technology have further improved the effectiveness and safety of this treatment modality. Some notable developments include:
- Locking Plate Systems: These systems provide enhanced stability and reduce the risk of screw loosening.
- Low-Profile Plates: Thinner plates minimize soft tissue irritation and reduce the risk of plate exposure.
- Resorbable Plates: While not made of titanium, these plates offer an alternative for specific cases where hardware removal is desired.
- 3D-Printed Custom Plates: Advanced imaging and 3D printing technologies allow for the creation of patient-specific titanium plates, optimizing fit and function.
Conclusion
Titanium plate for mandibular fracture has proven to be a highly effective method for treating mandibular fractures. Its ability to provide stable fixation, promote faster healing, and allow for early functional recovery has made it a preferred choice among maxillofacial surgeons. The biocompatibility and durability of titanium contribute to excellent long-term outcomes and patient satisfaction.
For more information about high-quality medical titanium products, including titanium plates for mandibular fracture treatment, please contact us at export@tiint.com. Our team of experts is dedicated to providing innovative solutions that improve patient outcomes and advance the field of maxillofacial surgery.










 2025-12-19 08:32:16
2025-12-19 08:32:16