Is Titanium Plate Surgery the Best Option for Hand Fracture Repairs?
 2025-12-23 08:25:40
2025-12-23 08:25:40
Hand fractures can be debilitating injuries that significantly impact our daily lives. When it comes to treating these fractures, titanium plate hand surgery has emerged as a popular and effective option. But is it truly the best choice for everyone? In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the pros and cons of titanium plate surgery for hand fractures, compare it to alternative treatments, and help you understand when it might be the most suitable option.
|
|
|
Grasping Titanium Plate Hand Surgery
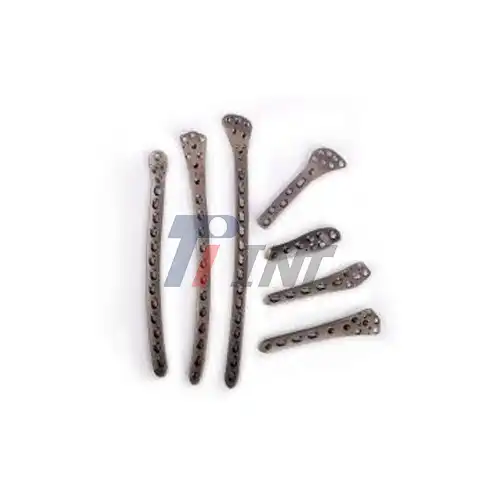
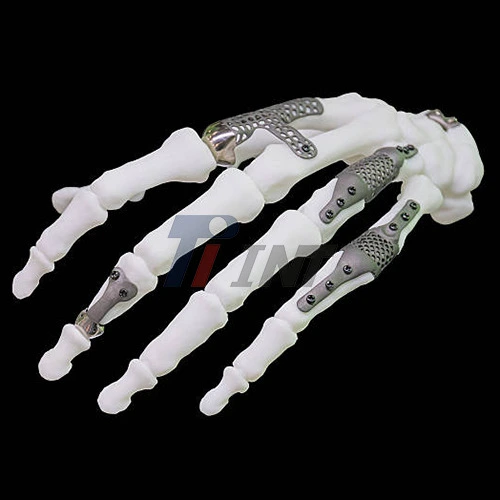
Titanium plate hand surgery is a procedure used to repair complex fractures in the hand. It involves the placement of a small titanium plate across the fractured bone, which is then secured with screws. This method provides stability to the fracture site, allowing for proper healing and alignment of the bone. The use of titanium in medical implants has revolutionized orthopedic surgery. Titanium is renowned for its biocompatibility, meaning it's well-tolerated by the human body. It's also corrosion-resistant and has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it an ideal material for surgical implants.
During the procedure, the surgeon makes an incision to access the fractured bone. The titanium plate is then carefully positioned and secured with screws. This internal fixation method provides immediate stability to the fracture, often allowing for earlier mobilization and potentially faster recovery times.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Titanium Plate Hand Surgery
Like any surgical procedure, titanium plate hand surgery comes with its own set of benefits and potential drawbacks. Understanding these can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment options.
Advantages:
- Stability: Titanium plates provide excellent stability to the fractured bone, which can lead to better alignment and healing.
- Early Mobilization: The stability provided by the plate often allows for earlier movement of the hand, which can be crucial for preventing stiffness and maintaining function.
- Precision: The use of plates and screws allows for precise positioning of bone fragments, which is particularly beneficial in complex fractures.
- Durability: Titanium is known for its strength and longevity, meaning the implant can provide long-term support if needed.
- Biocompatibility: Titanium is well-tolerated by the body, reducing the risk of adverse reactions.
Disadvantages:
- Invasiveness: As a surgical procedure, it carries risks associated with anesthesia and infection.
- Recovery Time: While early mobilization is possible, full recovery can still take several weeks to months.
- Potential for Hardware Irritation: Some patients may experience discomfort from the plate, particularly if it's near tendons or ligaments.
- Cost: Surgical procedures are generally more expensive than non-surgical treatments.
- Potential Need for Removal: In some cases, the hardware may need to be removed in a subsequent surgery.
Alternatives to Titanium Plate Hand Surgery
While titanium plate hand surgery is an effective treatment for many hand fractures, it's not always the first or only option. Several alternatives exist, each with its own set of pros and cons:
Cast Immobilization
For simple, non-displaced fractures, a cast may be sufficient. This non-invasive method involves immobilizing the hand and wrist to allow the bone to heal naturally. While it avoids surgery, it may require a longer period of immobilization and can lead to stiffness.
External Fixation
This method uses pins or wires inserted through the skin and attached to an external frame. It's often used for open fractures or severely comminuted (shattered) fractures. While less invasive than internal fixation, it can be cumbersome and may increase the risk of pin-site infections.
K-Wire Fixation
Kirschner wires (K-wires) can be used to hold bone fragments in place. This method is less invasive than plate fixation but may not provide the same level of stability. K-wires are often removed after the bone has healed.
Screws Without Plates
In some cases, screws alone can be used to fixate fractures. This method is less invasive than plate fixation but may not be suitable for all types of fractures.
Non-Surgical Management
For certain stable fractures, non-surgical management with careful monitoring and hand therapy may be appropriate. This approach avoids the risks of surgery but may not be suitable for complex or unstable fractures.
When is Titanium Plate Hand Surgery the Best Option?
Titanium plate hand surgery is often considered the best option in certain scenarios:
- Unstable Fractures: When a fracture is unstable or likely to displace during healing, plate fixation can provide the necessary stability.
- Comminuted Fractures: For fractures with multiple bone fragments, plates can help hold everything in proper alignment.
- Intra-articular Fractures: Fractures that extend into a joint often require precise reduction and stable fixation to prevent post-traumatic arthritis.
- Malunions or Nonunions: In cases where a fracture has healed incorrectly or failed to heal, plate fixation may be used in corrective surgery.
- High-Demand Patients: For patients who need to return to high-level activities quickly, the stability provided by plate fixation can be beneficial.
The decision to proceed with titanium plate hand surgery should always be made in consultation with an experienced hand surgeon. They will consider factors such as the patient's age, overall health, lifestyle, and the specific characteristics of the fracture.
The Importance of Proper Aftercare
Regardless of the treatment method chosen, proper aftercare is crucial for optimal recovery from a hand fracture. This typically includes:
- Hand Therapy: Working with a certified hand therapist can help restore range of motion, strength, and function.
- Pain Management: Following your doctor's recommendations for pain relief, which may include medication and ice therapy.
- Gradual Return to Activities: Slowly reintroducing daily activities as advised by your healthcare team.
- Follow-up Appointments: Regular check-ups to monitor healing and address any concerns.
Conclusion
Titanium plate hand surgery represents a significant advancement in the treatment of hand fractures. Its ability to provide stable fixation and potentially allow for earlier mobilization makes it an attractive option for many patients. However, it's not a one-size-fits-all solution. The best treatment for a hand fracture depends on numerous factors, including the nature of the fracture, the patient's overall health, and their functional needs. While titanium plate surgery offers many benefits, alternative treatments may be more appropriate in certain cases.
For more information about medical titanium products used in orthopedic surgeries, including those for hand fractures, you can reach out to Baoji INT Medical Titanium Co., Ltd. at export@tiint.com. With over 30 years of experience in titanium material research, development, and production, INT provides high-quality medical titanium materials that meet international standards and certifications.
References
1. Diaz-Garcia, R. J., & Chung, K. C. (2012). The Evolution of Distal Radius Fracture Management: A Historical Treatise. Hand Clinics, 28(2), 105-111.
2. Hak, D. J., & Golladay, G. J. (2000). Olecranon fractures: treatment options. The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 8(4), 266-275.
3. Jakubietz, R. G., Gruenert, J. G., & Jakubietz, M. G. (2012). The use of beta-tricalcium phosphate bone graft substitute in dorsally plated, comminuted distal radius fractures. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, 7(1), 24.
4. Jupiter, J. B., Marent-Huber, M., & LCP Study Group. (2009). Operative management of distal radial fractures with 2.4-millimeter locking plates. A multicenter prospective case series. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume, 91(1), 55-65.
5. Obert, L., Loisel, F., Gasse, N., & Lepage, D. (2015). Distal radius anatomy applied to the treatment of wrist fractures by plate: a review of recent literature. SICOT-J, 1, 14.