Why Do Some People Need a Titanium Plate in Their Head?
 2025-12-31 11:56:20
2025-12-31 11:56:20
When it comes to medical advancements, titanium has emerged as a game-changing material, especially in the field of neurosurgery. The use of a titanium plate in head has become increasingly common, offering hope and healing to individuals facing various cranial challenges. But what exactly leads to the need for such an intervention? Let's delve into the fascinating world of cranial titanium plates and explore the reasons behind their use.
|
|
|
Comprehending Cranial Titanium Plates
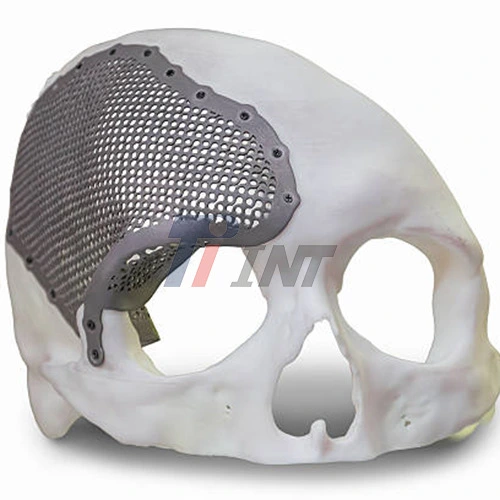
Before we explore the reasons for needing a titanium plate in the head, it's crucial to understand what these plates are and how they function. Cranial titanium plates are thin, malleable sheets of titanium specifically designed to repair or protect the skull. These plates are custom-shaped to fit the unique contours of a patient's skull, ensuring a perfect fit and optimal functionality.
The use of titanium in medical implants, including cranial plates, has revolutionized the field of neurosurgery. Titanium's biocompatibility, strength, and lightweight nature make it an ideal material for these applications. The human body generally accepts titanium implants without adverse reactions, reducing the risk of complications and improving long-term outcomes.
Cranial titanium plates serve various purposes, from protecting the brain after surgery to reconstructing damaged areas of the skull. These plates can be permanent fixtures or temporary measures, depending on the specific medical condition and treatment plan.
Medical Conditions Requiring Titanium Plates in the Head
Several medical conditions and situations may necessitate the use of a titanium plate in head. Understanding these circumstances can shed light on the importance of this medical intervention:
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): Severe head injuries from accidents, falls, or sports-related incidents can result in skull fractures or the need for surgical intervention. In such cases, titanium plates may be used to repair or reinforce damaged areas of the skull, providing protection for the healing brain.
- Brain Tumors: The surgical removal of brain tumors often requires creating an access point through the skull. After tumor removal, a titanium plate may be used to close the surgical site, ensuring proper healing and protection of the brain.
- Congenital Skull Deformities: Some individuals are born with skull abnormalities that require surgical correction. Titanium plates can be used to reshape and stabilize the skull, improving both function and appearance.
- Craniosynostosis: This condition occurs when a baby's skull bones fuse prematurely, potentially restricting brain growth. Surgical intervention, often involving the use of titanium plates, can help correct the skull shape and allow for normal brain development.
- Hydrocephalus: In cases of hydrocephalus, where excess cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the brain, a shunt may be placed to drain the fluid. Titanium plates can be used to secure the shunt and protect the surrounding area.
- Stroke-related Procedures: Certain stroke treatments, such as decompressive craniectomy, may require the temporary removal of a portion of the skull to relieve pressure. Once the swelling subsides, a titanium plate can be used to reconstruct the skull.
- Infections: Severe infections of the skull or underlying tissues may necessitate the removal of infected bone. Titanium plates can be used to reconstruct the affected area once the infection has been successfully treated.
The Titanium Plate Implantation Process
The process of implanting a titanium plate in head is a complex procedure that requires precision and expertise. Understanding this process can help demystify the procedure for those who may need it or are simply curious about medical advancements.
- Pre-operative Planning: Before the surgery, detailed imaging studies are conducted to assess the patient's skull structure and determine the exact specifications for the titanium plate. Advanced 3D modeling techniques may be used to create a custom-fit plate that matches the patient's unique anatomy.
- Anesthesia and Surgical Preparation: The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia to ensure patient comfort and stillness during the delicate operation. The surgical site is carefully prepared and sterilized to minimize the risk of infection.
- Incision and Access: The surgeon makes an incision in the scalp to access the area of the skull requiring the titanium plate. The incision's location and size depend on the specific condition being treated and the plate's intended placement.
- Plate Placement: The custom-designed titanium plate is carefully positioned over the affected area of the skull. The surgeon ensures that the plate fits precisely and provides the necessary support or protection.
- Fixation: Once properly positioned, the titanium plate is secured to the skull using specialized screws or other fixation methods. This step is crucial for ensuring the plate remains stable and fulfills its intended function.
- Closure and Recovery: After the plate is securely in place, the incision is closed using sutures or staples. The patient is then monitored closely during the immediate recovery period to ensure there are no complications.
- Post-operative Care: Following the surgery, patients typically undergo a period of recovery and rehabilitation. This may include pain management, wound care, and gradual return to normal activities under medical supervision.
The success of titanium plate in head implantation relies heavily on the skill of the surgical team and the quality of the materials used. Companies specializing in medical-grade titanium, such as Baoji INT Medical Titanium Co., Ltd., play a crucial role in providing the high-quality titanium necessary for these life-changing procedures.
The use of premium-grade titanium in cranial plates is paramount for several reasons:
- Biocompatibility: High-quality medical titanium minimizes the risk of adverse reactions, promoting better integration with the body's tissues.
- Durability: Superior titanium ensures long-lasting performance, reducing the need for future replacements or revisions.
- Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Premium titanium provides optimal strength while remaining lightweight, crucial for cranial applications where minimizing additional weight on the skull is important.
- Corrosion Resistance: Top-grade titanium resists corrosion, maintaining its integrity even in the challenging environment of the human body.
- Imaging Compatibility: High-quality titanium is compatible with various imaging modalities, allowing for clear post-operative monitoring and follow-up.
The impact of titanium plates on patients' lives cannot be overstated. These medical marvels not only protect the brain and aid in healing but also restore confidence and improve quality of life for many individuals. From children born with skull abnormalities to adults recovering from traumatic injuries, titanium plates offer a path to recovery and normalcy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the use of titanium plate in head is a fascinating intersection of medical necessity and technological innovation. From protecting vulnerable brain tissue to reconstructing damaged skulls, these remarkable devices play a crucial role in neurosurgery and patient care. As we continue to push the boundaries of medical science, the future looks bright for those who may need this life-changing intervention.
For more information about high-quality medical titanium products used in cranial plates and other medical applications, interested parties can reach out to Baoji INT Medical Titanium Co., Ltd. at export@tiint.com.
References
1. Zanotti, B., et al. (2019). Cranioplasty: Review of Materials. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery, 30(8), 2411-2417.
2. Neovius, E., & Engstrand, T. (2010). Craniofacial reconstruction with bone and biomaterials: review over the last 11 years. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery, 63(10), 1615-1623.
3. Winder, J., & Bibb, R. (2005). Medical rapid prototyping technologies: state of the art and current limitations for application in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 63(7), 1006-1015.
4. Shah, A. M., et al. (2014). Materials used in cranioplasty: a history and analysis. Neurosurgical Focus, 36(4), E19.
5. Cabraja, M., et al. (2009). Long-term results following titanium cranioplasty of large skull defects. Neurosurgical Focus, 26(6), E10.