The production of medical implants depends on 3mm sheets of titanium because they have great biocompatibility and mechanical properties. This thickness strikes the best balance between strength and ease of use for a range of medical purposes. A history of good performance in human body compatibility and long-term use has made 3mm titanium sheet trusted by surgeons and medical device manufacturers for orthopedic implants, dental work, and surgical tools.
|
|
|
Comprehending Medical Grade Titanium Materials
When medical device companies pick materials for devices that can be implanted, they run into problems that other industries don't see. It's hard for materials that need to stay strong and rust-free while also working with living tissues to get in the human body. Titanium that is 3mm thick has become the best choice for many things because of its great properties.
The two most common materials used in medicine are commercially pure titanium and Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Grade 23). The tensile strength of aluminum alloys is normally between 140 and 480 MPa. In contrast, these materials can withstand much more stress, between 345 and 1380 MPa. Because titanium is both strong and light, it is a good material for medical implants that need to hold up weight.
When titanium is exposed to oxygen, it can make a stable layer of oxide, which means that it is biocompatible. This natural barrier stops the release of harmful ions and promotes osseointegration, which is the direct connection between the implant's surface and the bone. Researchers found that titanium implants work better over time than implants made of other metals.
Core Medical Applications of 3mm Titanium Plates
Orthopedic Bone Plates and Tools to Fix Them
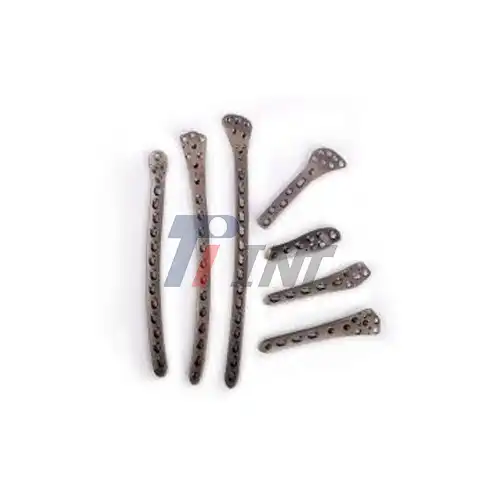
When orthopedic surgeons fix bones, they often use a 3mm titanium plate made from a 3mm titanium sheet. The thickness gives enough strength to hold broken bones in place while still allowing for exact shaping to fit the shape of the bone. These plates hold broken bones in place while they heal. They are especially helpful for complicated femur, tibia, and radius fractures.
The plate is made of titanium and is put on the surface of the bone in surgery. It is then held in place with screws made of titanium. This system spreads mechanical stress evenly across the fracture site so that the bone can heal properly. The 3mm thickness makes sure the plate won't bend or break under normal physical stresses. At the same time, it keeps a low profile that doesn't bother soft tissue.
Tools for Spinal Fusion
3mm sheets of titanium alloy are used to make interbody cages and stabilization rods for spinal fusion surgeries. These devices keep the spine in the right position and let bones grow through openings that are designed for this purpose. The titanium material makes it easier for bone to grow into it, which makes the segments of the spine permanently join together.
Surgeons like that titanium is radiolucent because it makes it easier to see the surgery in post-operative imaging. At 3mm thick, the plate is thin enough for minimally invasive surgery but offers enough support to handle the large forces that come from moving the spine.
Parts of a Dental Implant
Dental experts use 3mm sheets of titanium metal to make custom implant superstructures and abutments. The material's great ability to resist corrosion in the mouth means it will stay in good shape over time. Titanium is the best material for dental work because it can bond with jawbone tissue.
Precision machining of the titanium sheet is used to make parts that are just right for each patient. These pieces link the crown that you can see to the titanium root that was implanted. This gives the artificial teeth a strong base. The 3mm thickness gives enough strength while keeping the right look and shape.
Reconstruction Plates for the Skull and Face
After an injury or tumor removal, neurosurgeons and plastic surgeons use 3mm sheets of titanium to rebuild the skull. Because the material can be easily shaped, surgeons can make plates that fit the patient's skull perfectly. These implants help the brain and give support to soft tissues.
Before the procedure can be done, there needs to be a lot of planning that uses CT scans to make sure that the implants are made for each patient. During the surgery, the titanium plate is shaped so that it fits the problem area just right. The 3mm thickness gives enough protection while keeping the skull's natural shape.
Parts for Joint Replacement
In hip and knee replacement surgeries, 3mm titanium plates made from a 3mm titanium sheet are used in the acetabular cups and tibial baseplates. These parts are what the prosthetic joint and the patient's bone touch each other with. The titanium surface helps bone to grow into it, which makes for a strong and long-lasting connection.
Today's joint replacement designs have porous titanium surfaces that help biological fixation. The 3mm thickness gives the structure strength for weight-bearing uses while also allowing surface changes that make osseointegration better. Clinical studies show that this option leads to a longer life than similar options that are cemented in place.
Uses for implants in cardiovascular medicine
For making custom sternal closure plates and housings for cardiac devices, cardiac surgeons use titanium sheets that are 3 mm thick. Because the material is biocompatible, it can be safely used in the cardiovascular system for long periods of time. Its non-magnetic properties make sure that it can be used with MRI imaging.
After heart surgery, the sternum needs to be fixed in place very securely. Titanium plates are better than steel wires because they are stronger. The 3mm thickness is great at resisting wear and tear, which is important for standing up to millions of heartbeats over a patient's lifetime.
Uses for Reconstructive Surgery
Plastic and reconstructive surgeons use 3mm sheets of titanium alloy to rebuild faces that have been hurt or that have been damaged by congenital defects. The substance can be shaped with great accuracy to bring back the normal shape of the face while giving long-lasting support to the structure.
A lot of the time, these applications need to be made from scratch using patient imaging data. Titanium holds its shape over time, unlike other materials that can change shape slowly over time. The thin shape makes it less noticeable through the soft tissues on top of it.
Material Properties and Specifications
Understanding the technical details of 3mm titanium sheet helps makers choose the right materials for different uses. Grade 2 commercially pure titanium can be easily shaped into complex forms and resists corrosion very well, so it is great for use in situations where complicated shapes are needed.
Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Grade 23) has better strength and fatigue resistance than grades that are commercially pure. This alloy has 4% vanadium and 6% aluminum. It can handle tensile strengths of up to 860 MPa and is still very compatible with biological systems.
The way the surface is finished is very important to how well the implant works. Mirror-smooth to rough surfaces that help with tissue integration are some of the surface textures that manufacturers can make. Acid etching, sandblasting, and other surface treatments make micro-topographies that help cells stick.
Manufacturing and Quality Considerations
When medical device manufacturers use 3mm sheets of titanium for medical reasons, they must follow strict quality rules. ISO 13485 certification ensures medical device manufacturing meets standards. Every batch must be fully tested for chemical, mechanical, and surface properties.
The manufacturing process begins with vacuum arc remelting or electron beam melting of high-purity titanium. Biocompatible impurities are removed in these steps. Hot rolling gives bars the exact 3 mm thickness and size parameters.
Quality control includes surface inspection, ultrasonic testing, and mechanical strength testing. Everyone in the supply chain is responsible because the Certificate of Compliance links each sheet to its materials.
Processing Techniques for Medical Applications
3mm titanium sheet cutting requires special methods because the material hardens as it is worked. Manufacturers use waterjet cutting, laser cutting, or electrical discharge machining (EDM) to get exact shapes without creating zones that are affected by heat and could change the properties of the material.
To keep the 3mm titanium sheet welding clean, the welder must carefully control the environment. Welding with tungsten inert gas (TIG) in chambers filled with argon makes strong joints that are good for use in medical settings. Correct joint design and welding settings make sure that full penetration and the best mechanical properties are achieved.
Passivation and other post-processing treatments clean up the surface of the material and make it more resistant to corrosion. Stress relief annealing gets rid of stresses that are left over from forming operations. This makes sure that the final implant keeps its dimensions.
Benefits of 3mm Titanium Sheet in Medical Implants
3mm titanium sheet is great because it is good for the human body. Some metals can cause allergic reactions or make tissue inflamed, but titanium does not do that and actually works well with human tissue. This compatibility means that the implant is less likely to be rejected, which supports long-term success.
A 3mm sheet of titanium holds up better against corrosion than stainless steel in biological settings. The stable oxide layer stops ion leaching, which could hurt tissue or make the whole body toxic. This feature is very important for implants that stay in the body permanently.
Losing weight is another big benefit. Titanium has a density of 4.5 g/cm³, which is about half that of stainless steel. This makes things that are implanted in the body lighter. This feature helps the patient feel better and relieves stress on tissues close by.
Titanium has the most similar elastic modulus to human bone when compared to all other metals. This likeness lowers stress shielding, the practice of using stiff implants to support weights that would normally stress the bone. In the long run, this could lead to bone resorption.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Numerous international regulations govern medical titanium. Ti-6Al-4V ELI is covered by ASTM F136, while commercially pure titanium is covered by F67. These instructions cover microstructure, mechanics, and chemistry.
Before FDA approval, ISO 10993 requires many biocompatibility tests. These tests prevent patient systemic toxicity, irritation, sensitization, and cytotoxicity. Manufacturing companies must keep meticulous records to prove compliance.
Your European medical device should be CE-marked. This system ensures product quality, safety, and performance from manufacturing to disposal. Regular checks prove compliance.
Conclusion
The medical implant industry still depends on 3mm titanium sheets for a wide range of uses. Because it is so biocompatible, corrosion-resistant, and strong, it is used in orthopedic, dental, and cardiovascular implants. As medical technology gets better, titanium's role in helping patients stay healthy remains very important. Manufacturers looking for dependable, top-notch titanium, including 3mm titanium sheet options, should work with suppliers who know a lot about medical device manufacturing. Because it has a long history of success in that role and is still being used in new ways, titanium will continue to be the best material for medical implants that improve people's lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How are commercially pure titanium and Ti-6Al-4V ELI used in medicine different?
A: Commercially pure titanium is weaker but resists corrosion and works well with the body. Ti-6Al-4V ELI is stronger, fatigue-resistant, and biologically compatible. This is best for strong things like orthopedic implants.
Q2: Does a 3-mm thickness increase affect titanium medical implant function?
Three millimeters is the best thickness for strength and usability. It can be machined and formed precisely and is strong enough for most medical uses. This thickness is fine and won't hurt soft tissues.
Q3: What can be done to top 3mm titanium medical implant sheets?
A: Passivation prevents surface breakdown, acid etching helps cells stick, sandblasting roughens the surface, and hydroxyapatite improves osseointegration when the surface touches bone.
Q4: What quality papers should I look for in medical-grade titanium sheet?
A: Medical device manufacturing requires ASTM F67 or F136 and ISO 13485 certification. You should also request full material certificates with chemical, mechanical, and biocompatibility test results. Your market may require FDA and CE marking papers.
Q5: How can I store and handle medical 3mm titanium sheet?
A: Keep the titanium sheet dry and away from sharp objects. Carbon steel tools should not touch clean surfaces. Always know where things came from and don't scratch surfaces when moving and storing.
Q6: How long does it take to get custom 3mm titanium sheets for medical devices?
The number of items, how they are made, and the certifications required all affect how long it takes. Standard grades arrive in 2–4 weeks. It could take eight weeks for a special alloy or processing. Planning ahead and stocking up helps keep production on track.
Choose Baoji INT Medical Titanium for Premium 3mm Titanium Sheet Supplier Solutions
Baoji INT Medical Titanium Co., Ltd. is a top maker of 3mm titanium sheets. They have more than twenty years of experience working with medical titanium materials. We offer a wide range of products, including commercially pure titanium, Ti6Al4V ELI, and custom titanium alloys with different specs that can meet your exact needs. For medical device applications, we uphold strict quality control and give full proof of certification. Trust our knowledge to provide dependable, high-quality materials that meet the strict requirements of making medical implants. To talk about your exact material needs, please email us at export@tiint.com.
References
1. Brunette, D.M., Tengvall, P., Textor, M., & Thomsen, P. (2001). Titanium in Medicine: Material Science, Surface Science, Engineering, Biological Responses and Medical Applications. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
2. Geetha, M., Singh, A.K., Asokamani, R., & Gogia, A.K. (2009). Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants – A review. Progress in Materials Science, 54(3), 397-425.
3. Liu, X., Chu, P.K., & Ding, C. (2004). Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports, 47(3-4), 49-121.
4. Niinomi, M. (2008). Mechanical biocompatibilities of titanium alloys for biomedical applications. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 1(1), 30-42.
5. Rack, H.J., & Qazi, J.I. (2006). Titanium alloys for biomedical applications. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 26(8), 1269-1277.
6. Williams, D.F. (2008). On the mechanisms of biocompatibility. Biomaterials, 29(20), 2941-2953.










 2026-01-21 09:15:28
2026-01-21 09:15:28