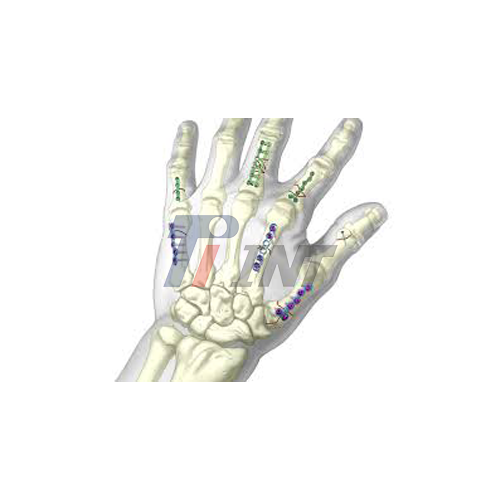
How Does Titanium Plate Surgery Improve Recovery Time in Hand Injuries?
 2025-12-22 09:36:10
2025-12-22 09:36:10
Hand injuries can be debilitating, affecting our ability to perform everyday tasks and significantly impacting our quality of life. When it comes to treating severe hand injuries, titanium plate hand surgery has emerged as a game-changer in the field of orthopedics. This innovative surgical technique not only aids in the proper healing of fractured bones but also substantially reduces recovery time, allowing patients to regain functionality faster than ever before. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the world of titanium plate hand surgery, its benefits, and how it revolutionizes the recovery process for hand injury patients.
|
|
|
Comprehending Titanium Plate Hand Surgery
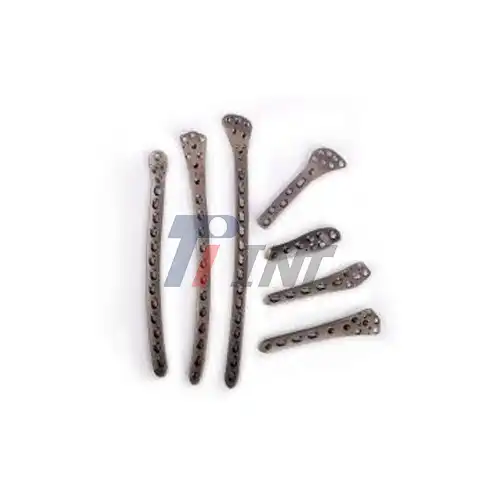
Titanium plate hand surgery is a surgical procedure that involves the use of titanium plates and screws to stabilize and support fractured bones in the hand. This technique is particularly effective for complex fractures, multiple bone injuries, or cases where traditional casting methods may not provide adequate support. The surgery typically involves making an incision to access the fractured bone, carefully aligning the bone fragments, and then securing them in place using titanium plates and screws. These implants act as an internal scaffold, providing the necessary stability for the bone to heal properly.
One of the key advantages of using titanium in these procedures is its biocompatibility. Titanium is well-tolerated by the human body, rarely causing adverse reactions or rejections. This characteristic makes it an ideal material for medical implants, including those used in hand surgeries.
Moreover, titanium's strength-to-weight ratio is exceptional. It's strong enough to provide robust support to the healing bone while being lightweight enough not to impede hand movement once recovery is complete. This balance of properties contributes significantly to the improved recovery times associated with titanium plate hand surgery.
The Impact of Titanium Plate Hand Surgery on Recovery Time
The introduction of titanium plate hand surgery has markedly improved recovery times for patients with hand injuries. This improvement can be attributed to several factors:
- Enhanced Stability: Titanium plates provide superior stability to the fractured bone compared to traditional casting methods. This stability allows for earlier mobilization of the hand, which is crucial for preventing stiffness and promoting healing.
- Reduced Immobilization Period: With titanium plate fixation, the need for prolonged immobilization is significantly reduced. Patients can often begin gentle movements and exercises much sooner than with other treatment methods, helping to maintain flexibility and strength in the hand.
- Precision in Bone Alignment: Titanium plate hand surgery allows surgeons to achieve more precise alignment of bone fragments. This precision reduces the likelihood of malunion (improper healing of the bone), which can lead to long-term functional issues and extended recovery times.
- Minimized Soft Tissue Damage: The surgical techniques used in titanium plate hand surgery are often less invasive than traditional open reduction methods. This approach results in less soft tissue damage, leading to reduced post-operative pain and swelling, and ultimately, faster healing.
- Accelerated Bone Healing: Some studies suggest that the presence of titanium implants may actually stimulate bone growth. This phenomenon, known as osseointegration, can contribute to faster and more robust bone healing.
By addressing these aspects, titanium plate hand surgery not only improves the quality of bone healing but also significantly reduces the overall recovery time. Patients often experience a quicker return to daily activities and work, minimizing the economic and personal impact of their injury.
Rehabilitation and Long-Term Outcomes After Titanium Plate Hand Surgery
While titanium plate hand surgery can significantly accelerate recovery, the rehabilitation process remains a crucial component of the overall treatment plan. The goal of rehabilitation is to restore strength, flexibility, and function to the injured hand while ensuring proper healing of the bone.
Typically, the rehabilitation process begins shortly after surgery, with the exact timing depending on the nature and severity of the injury. Early interventions often include:
- Gentle Range of Motion Exercises: These exercises help prevent stiffness and maintain joint mobility. They are usually started within the first few days post-surgery, under the guidance of a hand therapist.
- Edema Control: Techniques to manage swelling, such as elevation and compression, are implemented to reduce pain and improve mobility.
- Wound Care: Proper care of the surgical site is essential to prevent infection and ensure optimal healing.
- As healing progresses, the rehabilitation program intensifies, incorporating:
- Strengthening Exercises: Gradual introduction of exercises to rebuild muscle strength in the hand and forearm.
- Functional Activities: Incorporation of daily living activities to improve dexterity and hand function.
- Scar Management: Techniques to minimize scarring and maintain skin elasticity around the surgical site.
The long-term outcomes of titanium plate hand surgery are generally very positive. Most patients experience a full return to function, with minimal to no long-term limitations. The titanium plates and screws used in the surgery are typically left in place permanently, as they do not interfere with hand function and removal would require additional surgery.
It's worth noting that the success of titanium plate hand surgery and the subsequent recovery process heavily depends on the quality of the implants used. This is where companies like Baoji INT Medical Titanium Co., Ltd. play a crucial role. With their extensive experience in producing high-quality medical titanium materials, they ensure that surgeons have access to the best possible implants for these procedures.
The company's commitment to research and development in titanium materials ensures that they stay at the forefront of medical implant technology. This dedication translates directly to improved patient outcomes, as surgeons can rely on high-quality, innovative implants for their procedures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, titanium plate hand surgery represents a significant advancement in the treatment of hand injuries. By providing enhanced stability, allowing for earlier mobilization, and promoting faster bone healing, this technique dramatically improves recovery times for patients. The use of high-quality titanium implants, such as those produced by INT, further ensures the success of these procedures.
As research in this field continues to evolve, we can expect even more improvements in surgical techniques and implant materials, potentially leading to even faster recovery times and better long-term outcomes for patients with hand injuries. For more information about medical titanium products used in hand surgery and other orthopedic applications, please contact INT at export@tiint.com. Their team of experts can provide detailed information about their product range and how it can benefit both medical professionals and patients in the field of orthopedic surgery.
References
1. Garg, R., & Kragh, J. F. (2019). Bone Plate Fixation. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
2. Gautschi, O. P., Frey, S. P., & Zellweger, R. (2007). Bone morphogenetic proteins in clinical applications. ANZ journal of surgery, 77(8), 626-631.
3. Kamath, J. B., Jayasheelan, N., Mundargi, A. V., & Sujir, P. (2012). Fractures of the hand. Indian Journal of Plastic Surgery, 45(02), 289-297.
4. Keil, H., Beisemann, N., Schnetzke, M., Vetter, S. Y., Grützner, P. A., & Franke, J. (2018). Intraoperative assessment of reduction and implant positioning in proximal humeral fractures: How to use the C-arm efficiently. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, 32(1), e20-e26.
5. Loisel, F., Burnier, M., Bourgeois, M., Rochet, S., Lepage, D., Sarlieve, P., ... & Obert, L. (2018). Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for proximal humerus fractures: A prospective study describing principles and technique. SICOT-J, 4.