Lightweighting Medical Devices with Advanced Titanium Bars
 2026-02-05 10:12:39
2026-02-05 10:12:39
The medical device business is using lightweighting technology more and more to make devices more comfortable for patients and better at their jobs while still meeting strict safety standards. Advanced medical titanium bar materials have become the best choice for gadget makers who want to cut down on weight without sacrificing strength. These specially made bars are very strong, biocompatible, and resistant to rust, which makes them perfect for use in next-generation medical devices. Professionals in global business-to-business buying know that choosing high-quality titanium bars is the best way to meet the needs of the industry for creativity, longevity, and strict legal compliance in many markets.
|
|
|
Understanding Medical Titanium Bars and Their Advantages
Medical titanium bars are a big step forward in the making of safe materials. They were made to meet the special needs of modern healthcare uses. These precisely made bars are made from advanced titanium alloys, such as Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-6Al-4V ELI grades, which have been used in hospitals and clinics around the world and shown to work very well.
Superior Material Properties Drive Performance
Medical-grade titanium bars have a lot of benefits that come from the way the material is made. Titanium is a great material for reducing weight because it has a density of only 4.51 g/cm³, while stainless steel's density is 8 g/cm³. For example, this means that the strength-to-density ratio is 76 kN·m/kg, which is 20% better than regular stainless steel. Titanium has a low elastic modulus—about half that of stainless steel—which makes its qualities more like those of real bone. This means that it doesn't hide stress as well in orthopedic uses.
Another important benefit is that it doesn't wear down easily. This is especially important for implants that are loaded and unloaded many times over the course of their service life. Medical titanium bars are very strong and don't break easily even when things are changing. This means they will work well for a long time in physiologically demanding settings. The biocompatibility of these materials lowers the chance of bad reactions in tissues, which helps them fit in better with the living things around them.
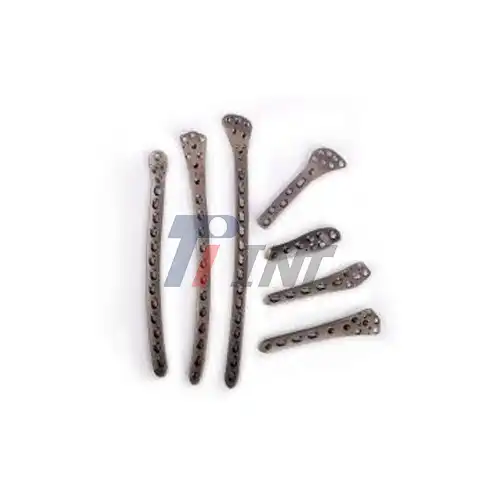
Diverse Applications Across Medical Sectors
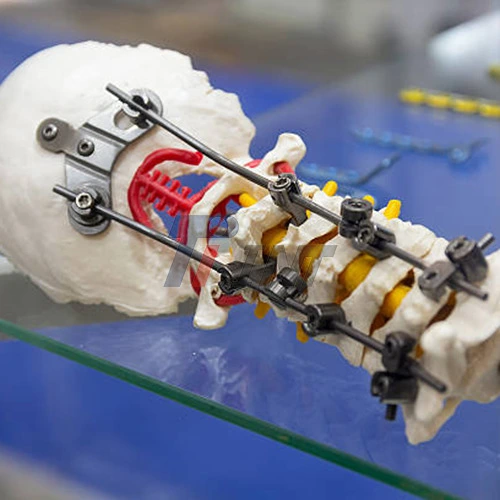
There are many uses for medical titanium bars in the healthcare field, from joint implants to surgery tools. In spine surgery, titanium plates that are light provide the skeletal support that is needed while also lowering the total mass of the implant. The material is biocompatible and doesn't rust, which are both useful in dental uses, especially in implant systems where long-term safety is important. Surgical tools made from these bars are easier to handle because they are lighter, which makes surgeons more comfortable during long procedures.
Comparing Medical Titanium Bars with Competing Materials
Material selection for medical device manufacturing requires careful evaluation of performance characteristics, cost considerations, and regulatory compliance requirements. Understanding how titanium bars compare to alternative materials helps procurement teams make informed decisions that align with specific project requirements and budget constraints.
Performance Benchmarking Against Alternatives
When looking at different materials, stainless steel is still often chosen because it costs less at first. Titanium's better resistance to rust, on the other hand, is very useful in biological settings where long-term stability is very important. Cobalt-chrome metals are very strong, but they don't have the good elastic stiffness qualities of titanium. The following list shows the main differences: Due to its non-ferromagnetic features, titanium can be used in magnetic resonance imaging techniques. This trait is very important for people who need to go for regular MRI checks after getting implants. Titanium's thermal qualities also help keep patients comfortable. Its lower thermal conductivity makes treatments less painful because of temperature changes.
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Procurement Teams
Even though titanium bars usually cost more up front than stainless steel bars, the total cost of ownership often works out better for titanium because it lasts longer, needs fewer repairs, and improves patient results. Titanium-based devices have longer service lives, which can more than cover their initial material costs by cutting down on replacement surgeries and the medical costs that come with them. International standards for medical devices are met by quality approvals like ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485:2016, and EU CE marking. These approvals give purchasing managers faith that materials can be tracked and that quality will be the same from one production batch to the next.
Procurement and Supply Chain Considerations for Medical Titanium Bars
Successful procurement strategies for medical-grade titanium bars require comprehensive supplier evaluation and supply chain management approaches that prioritize quality, reliability, and regulatory compliance. Understanding market dynamics and supplier capabilities enables procurement teams to establish robust sourcing relationships that support long-term manufacturing objectives.
Supplier Evaluation Criteria
Checking the seller's manufacturing skills and quality control systems is the first step in a good supplier evaluation. A lot of well-known suppliers have a lot of different certifications, such as ISO 9001:2015 for quality management and ISO 13485:2016 for medical device quality systems. Other things that affect the dependability of the supply chain are production capacity, the regularity of wait times, and the ability to provide expert help. Geography is a big part of planning the supply chain, especially when it comes to sending operations and the rules for customs when buying from other countries. Suppliers that offer customization services are very helpful for unique uses that need non-standard sizes or finishes on the surface.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
Material traceability paperwork helps with quality control processes all along the producing chain and makes sure that medical device rules are followed. Reliable providers give out thorough material certificates for each production batch that show the chemical make-up, mechanical qualities, and handling history. Sample testing methods let buying teams check the features of materials before making big purchases. This method lowers the risk while making sure that the material specs match the needs of the application. Setting clear quality deals with sellers helps make sure that the traits of materials stay the same from one delivery to the next.
Manufacturing and Quality Assurance of Medical Titanium Bars
The manufacturing process for medical titanium bars involves sophisticated metallurgical techniques and rigorous quality control measures to ensure consistent material properties and regulatory compliance. Understanding these processes helps procurement professionals evaluate supplier capabilities and make informed sourcing decisions.
Production Process Excellence
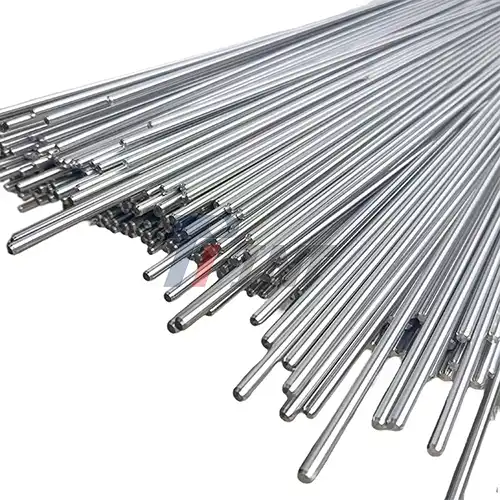
The process of making titanium starts with high-purity fuel that goes through controlled melting and alloying steps to get the exact chemical makeups needed. Using advanced casting and extrusion methods, the raw material is shaped into bars with precise surface and size limits. To meet the needs of medical devices, heat treatment methods improve the texture and dynamic qualities. As part of quality control, the tensile strength, stretch, and wear resistance traits are tested in detail. Ti6Al4V ELI grades must have a tensile strength of at least 895 MPa and a stretch number greater than 10%. Different surface finishing choices, such as buffed and sanded processes, meet the needs of different applications and improve biocompatibility.
Regulatory Compliance and Testing Standards
Medical-grade titanium bars go through a lot of biocompatibility testing based on ISO 10993 guidelines to make sure they are safe and compatible with flesh. Protocols for mechanical testing check wear resistance under situations that are similar to how the body normally loads things. These thorough testing programs make sure that materials meet the strict rules for medical devices sold around the world. Documentation tools keep track of everything from the source of the raw materials to the end steps of processing. This careful record-keeping helps with regulatory applications and gives the proof needed for medical device clearances in many foreign markets.
Company Introduction and Product Overview
After more than 20 years of specialized experience in the titanium business, Baoji INT Medical Titanium Co., Ltd. has become a top maker of advanced medical titanium bars. Our company was started in 2003 by Mr. Zhan Wenge, who has more than 30 years of experience in the titanium business. It has grown into a leading research, development, and production center for medical titanium materials.
Comprehensive Product Portfolio
Our product range encompasses pure titanium, Ti6Al4V, and Ti6Al4V ELI titanium bars in diameters ranging from 6 mm to 150 mm with lengths extending from 1000 mm to 3000 mm. These specifications accommodate diverse medical device manufacturing requirements while maintaining consistent quality standards across all product lines. Surface treatment options include polished and sandblasted finishes to meet specific application needs.
Advanced manufacturing capabilities enable us to provide customized solutions for OEM and ODM partners requiring specialized dimensions or properties. Our technical team collaborates closely with customers to develop tailored material solutions that optimize device performance while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Quality Certifications and Standards
Every product from our facility completes ISO 9001:2015 international quality system certification, ISO 13485:2016 medical device quality management system certification, and EU CE safety certification. These certifications demonstrate our commitment to maintaining the highest quality standards and regulatory compliance across international markets.
Our comprehensive service portfolio extends beyond material supply to include technical consultation, material selection guidance, and quality control documentation. This holistic approach supports customer success while building long-term partnerships based on trust and reliability.
Conclusion
Using improved titanium bars to make medical devices lighter is a big chance for companies that want to improve product performance while still meeting strict safety and regulatory standards. Medical-grade titanium materials are clearly better than other options because they are stronger, lighter, and don't wear down easily. They are also biocompatible. To make sure that reliable material buying supports long-term business goals and patient safety standards, it's important to carefully evaluate suppliers, follow quality assurance procedures, and understand how things are made.
FAQ
What titanium grades are most suitable for medical implants?
Ti6Al4V and Ti6Al4V ELI are the medical-grade titanium metals that are most often used for implants. These metals, which are made up of 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium, are very biocompatible and have good mechanical qualities. Ti6Al4V ELI has higher purity levels that make it even more compatible with tissue. This makes it perfect for long-term implant uses.
How does biocompatibility compare between titanium and stainless steel?
Titanium demonstrates superior biocompatibility compared to stainless steel due to its non-toxic, non-allergenic properties and excellent corrosion resistance in biological environments. The stable oxide layer that forms on titanium surfaces prevents metal ion release, reducing the risk of adverse tissue reactions. This makes titanium the preferred choice for permanent implants requiring long-term biological compatibility.
What certifications should I verify when selecting a titanium supplier?
Some important certifications are ISO 13485:2016 for medical device quality management and ISO 9001:2015 for quality management systems. Other important regional certifications include EU CE marks. Also, make sure that the materials meet the requirements of ASTM and AISI, are registered with the FDA if needed, and have been biocompatibility tested according to ISO 10993 standards.
Partner with Baoji INT Medical Titanium Co., Ltd. for Advanced Medical Solutions
Our wide selection of approved medical titanium bars at Baoji INT Medical Titanium Co., Ltd. is ready to help you with your efforts to make medical devices lighter. Our ISO-certified production methods and many years of experience in the field make sure that you can always count on us to provide you with high-quality products that meet your needs. As a reliable medical titanium bar provider, we offer OEM and ODM partners around the world unique solutions, expert support, and low prices. Contact our technical team at export@tiint.com to discuss your project requirements and discover how our advanced titanium materials can enhance your device performance while ensuring regulatory compliance and patient safety.
References
1. Geetha, M., Singh, A. K., Asokamani, R., & Gogia, A. K. (2009). Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopedic implants–a review. Progress in Materials Science, 54(3), 397-425.
2. Niinomi, M. (2008). Mechanical biocompatibilities of titanium alloys for biomedical applications. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 1(1), 30-42.
3. Liu, X., Chu, P. K., & Ding, C. (2004). Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports, 47(3-4), 49-121.
4. Ryan, G., Pandit, A., & Apatsidis, D. P. (2006). Fabrication methods of porous metals for use in orthopedic applications. Biomaterials, 27(13), 2651-2670.
5. Long, M., & Rack, H. J. (1998). Titanium alloys in total joint replacement—a materials science perspective. Biomaterials, 19(18), 1621-1639.
6. Elias, C. N., Lima, J. H. C., Valiev, R., & Meyers, M. A. (2008). Biomedical applications of titanium and its alloys. JOM Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, 60(3), 46-49.