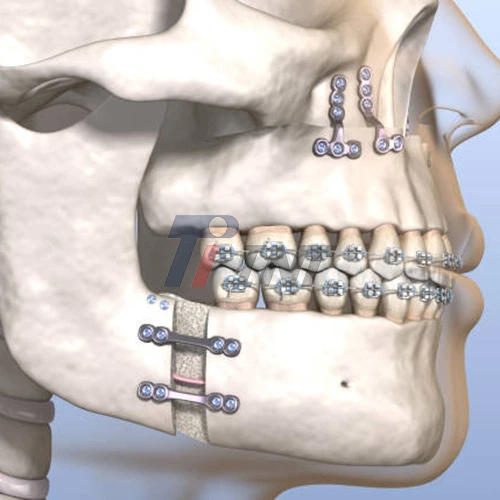
The Evolution of Mandibular Fracture Treatment
Historically, the treatment of mandibular fractures has undergone significant evolution. In the past, wire fixation and intermaxillary fixation were the primary methods used to stabilize fractures. However, these techniques often led to prolonged periods of jaw immobilization, causing discomfort and hindering normal oral function.
The advent of rigid internal fixation using plates and screws revolutionized the field of maxillofacial surgery. Among the materials used for internal fixation, titanium quickly rose to prominence due to its unique properties and biocompatibility.
Titanium plate for mandibular fractures have become increasingly sophisticated over time. Modern designs incorporate features that enhance their effectiveness and ease of use. For instance, some plates now have locking mechanisms that provide enhanced stability and reduce the risk of screw loosening.
Advantages of Titanium Plates in Mandibular Fracture Repair
The use of titanium plates in mandibular fracture repair offers numerous advantages over alternative materials and methods. These benefits have solidified titanium's position as the material of choice for internal fixation devices.
- Biocompatibility: One of the most crucial attributes of titanium is its exceptional biocompatibility. When a titanium plate for mandibular fracture is implanted, it rarely elicits an adverse immune response. This property significantly reduces the risk of rejection and post-operative complications.
- Strength and Durability: Titanium boasts an impressive strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for use in load-bearing applications such as mandibular fracture repair. Titanium plates can withstand the forces exerted during normal jaw function without deforming or breaking.
- Corrosion Resistance: The human body can be a harsh environment for implanted materials. Titanium's natural resistance to corrosion ensures that the plate remains intact and functional over extended periods, reducing the need for revision surgeries.
- Osseointegration: Titanium has the unique ability to integrate with bone tissue, a process known as osseointegration. This property enhances the stability of the fracture fixation and promotes faster healing.
- Radiolucency: Titanium plates are relatively radiolucent, meaning they allow X-rays to pass through with minimal interference. This characteristic is crucial for post-operative monitoring and assessment of fracture healing.
- Versatility: Titanium plates can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes, allowing surgeons to select the most appropriate plate for each specific fracture pattern and location.
The Surgical Process and Recovery with Titanium Plates
The surgical process for mandibular fracture repair using titanium plates typically involves several steps:
- Pre-operative Planning: Surgeons use imaging techniques such as CT scans to assess the fracture and plan the placement of titanium plates.
- Incision and Exposure: An incision is made to expose the fractured bone, either through an intraoral or extraoral approach, depending on the fracture location and complexity.
- Fracture Reduction: The fractured bone segments are carefully aligned to their proper anatomical position.
- Plate Application: The titanium plate for mandibular fracture is contoured to fit the bone's surface and secured using titanium screws.
- Wound Closure: Once the plate is in place, the surgical site is thoroughly irrigated, and the incision is closed.
Recovery following mandibular fracture repair with titanium plates is generally faster and more comfortable compared to traditional methods. Patients can often resume normal jaw function much sooner, leading to improved quality of life during the healing process.
While titanium plates for mandibular fractures have proven highly effective, ongoing research continues to refine and improve this treatment modality. Some areas of current investigation include:
- Surface Modifications: Researchers are exploring ways to modify the surface of titanium plates to further enhance osseointegration and reduce the risk of infection.
- Biodegradable Alternatives: While not yet as reliable as titanium, biodegradable plates are being developed that could eliminate the need for plate removal in certain cases.
- 3D Printing: Advancements in 3D printing technology are enabling the creation of patient-specific titanium plates, potentially improving fit and outcomes.
- Antibiotic-Coated Plates: To further reduce the risk of post-operative infections, some researchers are investigating the use of antibiotic coatings on titanium plates.
Despite these ongoing developments, titanium plates remain the gold standard for mandibular fracture treatment due to their proven track record of safety and efficacy.
The choice of implant material is crucial in maxillofacial surgery, and titanium has consistently demonstrated its superiority. When selecting a titanium plate for mandibular fracture repair, surgeons consider several factors:
- Plate Design: Different fracture patterns may require specific plate designs, such as compression plates, reconstruction plates, or miniplates.
- Plate Thickness: The thickness of the plate must be sufficient to provide adequate stability without being overly bulky.
- Screw Configuration: The number and arrangement of screw holes can affect the plate's stability and ease of application.
- Surface Treatment: Some titanium plates undergo surface treatments to enhance their performance or reduce the risk of complications.
The quality and consistency of titanium plates are paramount to ensure optimal surgical outcomes. Reputable manufacturers adhere to strict quality control measures and comply with international standards for medical devices.
While titanium plates for mandibular fractures have revolutionized treatment, their successful use depends on various factors beyond the material itself. These include:
- Surgical Skill: The expertise and experience of the surgeon play a crucial role in achieving optimal outcomes.
- Patient Compliance: Following post-operative instructions, including dietary restrictions and oral hygiene practices, is essential for proper healing.
- Overall Health: Factors such as nutrition, smoking status, and the presence of systemic diseases can influence the healing process.
- Timing of Surgery: In some cases, immediate fixation may be necessary, while in others, a delay may be beneficial to allow for the resolution of swelling.
As with any surgical procedure, the use of titanium plate for mandibular fractures carries some potential risks and complications. However, these are generally rare and can often be managed effectively. Possible complications include:
- Infection: While titanium is resistant to bacterial colonization, infections can still occur. Proper sterilization techniques and antibiotic prophylaxis help minimize this risk.
- Hardware Failure: In rare cases, the plate or screws may loosen or break, particularly if subjected to excessive force before complete healing.
- Malocclusion: Improper plate placement or fracture reduction can lead to changes in bite alignment.
- Nerve Injury: Care must be taken to avoid damage to nerves during plate placement, particularly the inferior alveolar nerve.
- Palpability: In some patients, especially those with thin soft tissue coverage, the plate may be palpable beneath the skin or mucosa.
The future of mandibular fracture treatment looks promising, with ongoing advancements in materials science and surgical techniques. While titanium plates currently hold the position as the gold standard, research into new materials and approaches continues. Some areas of investigation include:
- Nanostructured Titanium: Manipulating the structure of titanium at the nanoscale may lead to plates with even better mechanical properties and biocompatibility.
- Smart Materials: Researchers are exploring materials that can change properties in response to stimuli, potentially allowing for dynamic fracture fixation.
- Tissue Engineering: Combining titanium plates with growth factors or stem cells may enhance bone regeneration and accelerate healing.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Advancements in surgical instruments and imaging technologies may enable less invasive placement of titanium plates, reducing surgical trauma and improving recovery times.
Conclusion
Titanium plate for mandibular fractures have revolutionized the field of maxillofacial surgery, offering a combination of strength, biocompatibility, and versatility that is unmatched by other materials. Their use has significantly improved patient outcomes, reduced recovery times, and enhanced the overall quality of care in mandibular fracture treatment.
For those seeking high-quality titanium materials for medical applications, including mandibular fracture repair, Baoji INT Medical Titanium Co., Ltd. offers a comprehensive range of titanium products. With over 30 years of experience in the research, development, and production of titanium materials, INT has established itself as a leader in the medical titanium industry. To learn more about their products and services, interested parties can contact them at export@tiint.com.










 2025-12-22 09:31:53
2025-12-22 09:31:53